Did you know that boosting your mitochondrial health could slow aging by over 30%? While most of us focus on diet and exercise for vitality, few realize that the path to a longer, more energetic life begins deep within our cells—with the tiny, powerhouse structures called mitochondria. Understanding how to activate mitochondria is not just a scientific curiosity—it’s a life-changing approach to strengthening your immune system, maximizing your energy production, and promoting longevity. This comprehensive guide blends breakthrough research with practical steps so you can unlock your body’s potential and feel your best well into the future.
Unlocking Longevity: Why You Need to Activate Mitochondria
“Research shows that mitochondrial health can impact aging by more than 30%.”
Key reasons to activate mitochondria for longevity: Mitochondria drive energy production and protect against cellular decline.
The link between mitochondrial health and chronic disease: Poor mitochondrial function is tied to health conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and neurodegeneration.
Surprising roles mitochondria play: They’re not just about energy—mitochondria regulate metabolism, immune defense, and even lifespan.
When you focus on practices that activate mitochondria, you tap into the cell’s natural mechanism for creating adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the essential energy currency. A robust mitochondrial function doesn’t just provide more energy for your day; it defends your body from reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress that accelerate the aging process and create pathways for chronic disease. Aging itself, as highlighted by medical school research, is increasingly understood as a consequence of mitochondrial decline, so supporting these organelles ensures both immediate and long-term health benefits.
Mitochondrial health also influences mental clarity and physical stamina. By investing in strategies that support and activate mitochondria, you’re investing in stronger muscle cells, steadier mood, and healthy immune balance—resulting in better mental health, lower risk of chronic disease, and more years of vital living.
What You'll Learn About How to Activate Mitochondria (Overview)
The main benefits of supporting your mitochondria for energy, mental health, and resilience
Science-backed strategies to enhance mitochondrial function
Foods and nutrients that repair and strengthen mitochondria
How to spot and address mitochondrial dysfunction
Everyday, practical steps for activating mitochondria and maintaining consistent energy
This article delivers actionable knowledge so you can understand the role of mitochondria in energy production, identify factors that influence their performance, and put the latest research into practice for robust cellular health and exceptional longevity.
By the end, you’ll be equipped with all the resources to activate mitochondria—from key foods to specific exercises and cutting-edge therapies—helping you support your mitochondria and transform how you age, move, and think.
What Are Mitochondria and Why Do They Matter for Longevity?
Understanding Mitochondrial Function and Energy Production
Role of mitochondria in energy production: Mitochondria convert nutrients into ATP via the electron transport chain.
Mitochondrial function supports cellular health: Every human cell (except red blood cells) depends on mitochondria for efficient metabolism, repair, and immune resilience.
Mitochondria are known as the cell’s “powerhouses” because they are essential for energy production. These dynamic organelles act as the main generators of ATP through a process called oxidative phosphorylation, which happens along the electron transport chain. Every time you move, think, or even breathe, your mitochondria are hard at work converting carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into usable cellular energy. ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, powers all vital processes, from muscle cell contractions to neurotransmitter release in the brain.
The complex processes inside each mitochondrion not only fuel our muscle cells and organs, but also defend against harmful byproducts called reactive oxygen species. When functioning optimally, mitochondria ensure robust cellular function—supporting a smooth transport chain, regulating apoptosis (cell death), and orchestrating cell-signaling events vital for growth and repair. In short, supporting your mitochondria is foundational for peak physical and mental performance.
Mitochondrial Health and Its Impact on Lifespan
The connection between mitochondrial health and aging processes: Mitochondrial decline is linked to reduced ATP, impaired cell function, and accumulation of cellular damage throughout life.
Effects on mental health and physical vitality: Dysfunction leaves us feeling tired, lowers resilience to stress, and accelerates age-related degeneration in muscles, heart, and brain.
As we age, our mitochondria experience damage from environmental toxins, poor dietary habits, and naturally rising levels of oxidative stress. Studies consistently show that mitochondrial health is directly tied to the aging process: the less efficient your mitochondria, the faster issues like fatigue, frail muscle, and cognitive decline set in. Conversely, individuals with robust mitochondrial function often enjoy better memory, greater muscle mass, and increased longevity.
This isn’t just limited to physical vitality; mitochondria have a surprising influence on mental health. Research from leading medical schools links mitochondrial decline to disorders such as depression and anxiety, highlighting ATP production’s role in neurotransmitter synthesis and brain resilience. Prioritizing strategies that keep mitochondrial DNA intact and minimize oxidative stress can help slow down age-related decline, increase overall health span, and support your mitochondria so you feel years younger.
Factors That Influence Mitochondrial Health
Support Your Mitochondria: Genetics, Environment, and Lifestyle
Genetic factors in mitochondrial function: Inherited mutations in mitochondrial DNA can reduce energy output and increase disease risk.
Environmental toxins and oxidative stress: Pesticides, air pollution, and glyphosate exposure hinder electron transport chain efficiency, accelerating cellular aging.
Impact of exercise, nutrition, and sleep: Regular movement, a nutrient-rich diet, and restorative sleep protect and support your mitochondria for better energy and resilience.
Your mitochondria are shaped by both genetic inheritance and lifestyle. While some individuals may be born with less efficient mitochondrial DNA or higher susceptibility to mitochondrial dysfunction, most people’s risks can be drastically reduced by adopting the right daily habits. The single greatest threat remains oxidative stress: the accumulation of toxic reactive oxygen species from pollution, pesticides, tobacco, and even chronic stress. When left unchecked, these stressors cause significant mitochondrial damage and disrupt the electron transport chain, draining your energy reserves and leaving you prone to metabolic disease.
However, you have powerful tools to protect against this decline. Studies on human cell models and study participants across various demographics demonstrate that regular physical activity, anti-inflammatory nutrition, and adequate sleep can activate mitochondria and reverse some signs of cellular aging. Shielding your environment from toxins, reducing exposure to plastics, and making conscious choices about food all give your mitochondria the upper hand in the battle for longevity and health benefits.
Common Causes of Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Toxins, chronic stress, inflammation: Environmental chemicals, ongoing psychological pressure, and unchecked inflammation impair mitochondrial DNA, damaging the electron transport chain.
Poor diet and sedentary lifestyle: Highly processed foods, sugar, and inactivity limit the body’s ability to repair mitochondria and generate new ones (mitochondrial biogenesis).
One of the biggest culprits in the rise of chronic illness and accelerated aging is mitochondrial dysfunction. Medical literature highlights that environmental pollutants, unhealthy fats, and a lack of movement can all directly sabotage ATP production. This results in a cycle of fatigue, muscle weakness, and metabolic slowdown typical of an unhealthy lifestyle. For many, the link between environmental exposures—everything from pesticides to heavy metals—and mitochondrial decline is underestimated, underlining the importance of detoxification and mindful living.
Chronic stress and inflammation further increase reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, leading to persistent mitochondrial damage. Health conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and even neurodegenerative disorders often trace back to impaired oxidative phosphorylation and reduced capacity to support your mitochondria. Awareness of these risk factors empowers you to adopt daily practices that defend your cellular energy systems from further harm.
How to Activate Mitochondria: Evidence-Based Methods
Nutrition to Support Your Mitochondria and Energy Production
Mitochondria-boosting foods: Leafy greens, wild salmon, avocados, olive oil, blueberries, and a variety of nuts.
Essential nutrients: CoQ10 (coenzyme Q10), B vitamins, magnesium, and N-acetylcysteine (NAC) fortify the electron transport chain and enhance ATP production.

Dietary strategies are among the most effective ways to activate mitochondria. Foods rich in antioxidants heal mitochondrial damage and protect against oxidative stress by neutralizing reactive oxygen species. Leafy greens like spinach provide magnesium and B vitamins required for cellular energy, while wild salmon and nuts offer omega-3 fatty acids critical for maintaining the flexibility of mitochondrial membranes. Blueberries and other vibrantly colored fruits supply polyphenols, helping rejuvenate mitochondrial DNA and stimulate new mitochondria growth.
Research also supports supplementing with CoQ10 and NAC for individuals with chronic health conditions or high levels of physical stress. These dietary supplements help restore depleted electron transport chains, increase antioxidant availability, and protect the transport chain from further damage. Ultimately, a nutrient-dense, whole-food diet—rich in colorful plants, clean proteins, and healthy fats—makes a measurable difference to how well your muscle cells, brain, and heart perform each day.
Exercise and Lifestyle Strategies to Activate Mitochondria
HIIT vs. steady-state cardio: High-intensity interval training promotes rapid mitochondrial biogenesis with a shorter time investment; steady-state cardio supports gradual endurance improvements.
Benefits of strength training: Lifting weights encourages mitochondrial growth in skeletal muscle and amplifies cellular energy availability.
Role of sleep and circadian rhythm: Consistent, quality sleep directly boosts mitochondrial repair and daily ATP production.

Exercise is one of the most potent, free tools to support your mitochondria and catalyze new growth. Research confirms that even brief sessions of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) trigger surges in mitochondrial biogenesis, improving the number and efficiency of mitochondria in muscle cells. Regular strength training further boosts mitochondrial density, helping your body use glucose and fat for ATP more efficiently while protecting skeletal muscle during aging.
It’s not just about movement—adequate sleep and keeping your circadian rhythm in check play pivotal roles in mitochondrial repair. During deep sleep, your body performs essential maintenance on mitochondrial DNA, making recovery just as important as training. For maximum health benefits, aim for a blend of HIIT, steady-state cardio, and strength training, and prioritize at least 7-8 hours of sleep nightly to maximize energy production and enhance all aspects of mitochondrial and cellular health.
Supplements Proven to Enhance Mitochondrial Function
CoQ10, PQQ, carnitine, omega-3 fatty acids: These supplements are proven to improve mitochondrial function and energy capacity.
Scientific evidence and recommended dosages: Human studies report health benefit in dosages of 100–300mg CoQ10, 10–20mg PQQ, 500–2000mg carnitine, and 1000–3000mg fish oil daily—but always consult a medical professional before starting any supplement protocol.
Several dietary supplements offer promising support for mitochondrial health. Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) acts as a direct fuel for the electron transport chain, boosting ATP production and reducing symptoms of chronic fatigue. Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) promotes new mitochondrial growth and enhances the resilience of existing organelles. Carnitine supports fat metabolism within muscle cells and has been linked to improved exercise recovery and cardiovascular health.
Omega-3 fatty acids, especially from fish oil, provide structural support for mitochondrial membranes and decrease inflammation that can lead to mitochondrial dysfunction. When these supplements are paired with a balanced diet and active lifestyle, they synergistically help activate mitochondria, improve energy levels, and support your mitochondria for optimal health and longevity.
Symptoms of Mitochondrial Dysfunction: What to Watch For
Low energy and chronic fatigue
Muscle weakness
Poor mental health and cognitive issues
Signs of aging and metabolic slowdown

Recognizing the symptoms of mitochondrial dysfunction can help you take corrective action before cellular decline becomes irreversible. Classic signs include persistent fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest, generalized muscle weakness, and a noticeable drop in exercise tolerance. People with compromised mitochondrial health also struggle with brain fog, memory lapses, and mood swings—underlining the link between energy production, mental health, and cognitive vitality.
Early warning signs manifest as visible aging, metabolic slowdown, and sluggishness throughout the day. If you suffer from low cellular energy, frequent infections, unexplained pain, or slow recovery from physical activity, mitochondrial dysfunction could be the underlying cause. The good news? Many aspects of mitochondrial repair and activation are completely within your control, allowing you to support your mitochondria and reverse many early signs of decline.
Mental Health and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Links between mitochondrial function and depression, anxiety, brain fog
Mental health and mitochondrial function are intertwined in ways only recently understood by science. Research now suggests that impaired ATP production in neurons and glial cells undermines mood regulation, memory, and stress resilience. Individuals with a history of depression or anxiety disorders have been shown to have lower mitochondrial density and efficiency, which makes supporting your mitochondria crucial not just for your body, but for your mind.
Addressing mitochondrial dysfunction through nutrition, exercise, and targeted supplementation can help stabilize neurotransmitter production, reduce the effects of stress, and restore cognitive clarity. Interventions that reduce oxidative stress have demonstrated improvements in mental well-being, highlighting the tangible benefits of a comprehensive, mitochondria-first approach to both physical and mental health.
Foods That Repair and Activate Mitochondria
Top foods: wild salmon, spinach, broccoli, blueberries, nuts, olive oil
How antioxidants combat oxidative stress
Foods and Nutrients for Activating Mitochondria | ||
Food |
Key Nutrients |
Mitochondrial Health Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Wild Salmon |
Omega-3s, Selenium |
Reduces inflammation, protects membranes |
Spinach |
Magnesium, B vitamins |
Supports ATP production, antioxidant defense |
Broccoli |
Sulforaphane, Vitamin C |
Boosts detoxification, combats oxidative stress |
Blueberries |
Polyphenols, Vitamin K |
Repairs DNA, reduces inflammation |
Nuts |
Healthy Fats, CoQ10 |
Enhances electron transport, repairs membranes |
Olive Oil |
Polyphenols, Monounsaturated Fats |
Protects against cellular damage |

These foods aren’t just delicious—they’re fuel for your mitochondria. Nutrient-dense, antioxidant-rich whole foods deliver the antioxidants and phytonutrients needed to rebuild damaged mitochondria, protect against oxidative stress, and restore optimal cellular function. The powerful combination of healthy fats (like those in salmon and olive oil), vitamins, and minerals helps regulate the electron transport chain and offers continuous energy support.
Including a broad spectrum of colors and whole, unprocessed plant foods in your daily meals is the most effective diet-based way to repair and activate mitochondria. Regular consumption of leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, and berries not only improves mitochondrial health but also supports the aging process, mental health, and disease resistance.
Cutting-Edge Therapies and Future Trends to Activate Mitochondria
Red light therapy
NAD+ boosters
Intermittent fasting and autophagy
Mitochondrial transplants (research spotlight)
“Restoring mitochondrial health could be the key to reversing age-related decline.” – Leading scientist in mitochondrial research
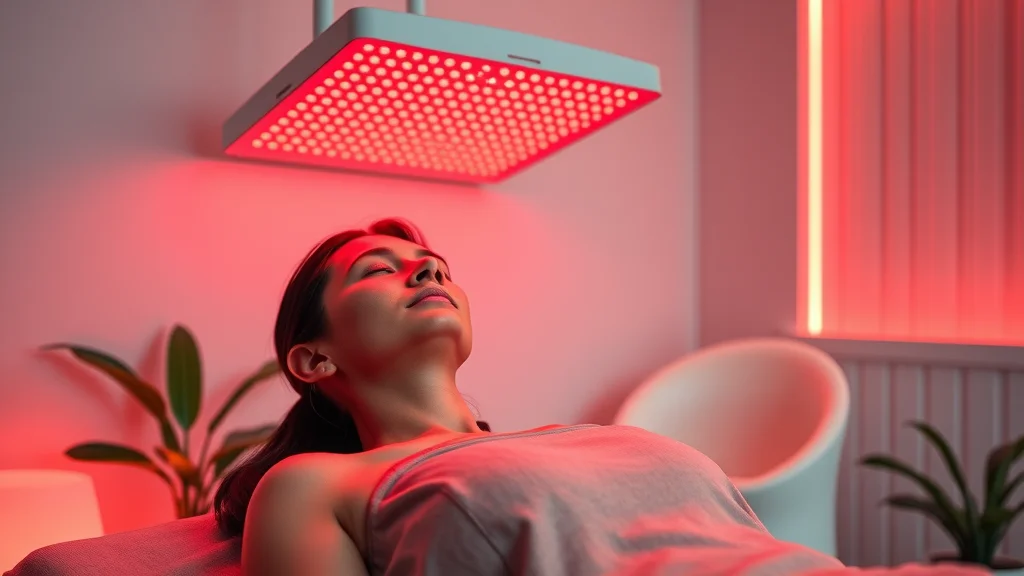

Wave after wave of innovation is unlocking new ways to activate mitochondria and reverse cellular aging. Red light therapy uses specific wavelengths to stimulate the electron transport chain, accelerating ATP production and recovery in both muscle cell and nervous tissue. NAD+ boosters—compounds like nicotinamide riboside—amplify cellular energy, triggering mitochondrial biogenesis and robust repair.
Intermittent fasting activates autophagy, the cleanup process where cells remove damaged mitochondria to make room for new, more efficient ones. While mitochondrial transplants are still in the research phase, early results suggest the potential for transforming treatment for complex chronic disease and metabolic disorders. Staying informed about these developments keeps you at the cutting edge of personalized longevity strategies and future health technologies.
Daily Practices to Support Your Mitochondria and Boost Energy Production
Actionable steps for morning, midday, and evening routines
Building sustainable habits for mitochondrial health
Morning: Start the day with a glass of water, stretch or walk in sunlight, and eat a balanced breakfast rich in healthy fats and antioxidants.
Midday: Prioritize nutrient-dense meals, take brief movement breaks to stimulate blood flow, and practice stress management (meditation or deep breathing).
Evening: Engage in gentle exercise, consume a light, antioxidant-rich dinner, and establish a calming bedtime routine for restorative sleep.

-
Checklist: How to Activate Mitochondria Every Day
Eat a diverse, plant-rich diet with healthy fats and lean protein
Incorporate HIIT and resistance training weekly
Prioritize quality sleep and hydration
Supplement with mitochondrial-supportive nutrients if needed (consult a healthcare provider)
Minimize exposure to toxins and process stress with mindfulness or breathwork
Try new longevity practices—like sauna, cold therapy, and intermittent fasting
Watch: “How to Activate Mitochondria for Improved Energy”—Explore visual tips and see step-by-step exercises and meal ideas that support your mitochondria in action.
People Also Ask: How do I activate my mitochondria?
Simple and proven methods to activate mitochondria today
Increase exercise intensity and frequency (including HIIT and resistance training)
Adjust your diet to focus on leafy greens, fatty fish, nuts, and berries
Consider a targeted supplement protocol under professional guidance (CoQ10, carnitine, omega-3s)
Answer: Practical steps and tips for activating mitochondria, including exercise, diet, and supplements
To activate mitochondria, add short bursts of interval training and daily movement, increase your intake of mitochondrial-supportive foods, reduce processed foods and sugars, and target key nutrients with safe, evidence-backed supplements. Small shifts in routine, such as drinking water first thing in the morning and meditating before bed, lay the groundwork for steady improvement in energy and resilience.
People Also Ask: What foods repair mitochondria?
List of top foods that support mitochondrial health
Antioxidant-rich berries, leafy greens (spinach, kale), and cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, Brussels sprouts)
Wild-caught fatty fish (like salmon), walnuts, and almonds
Extra virgin olive oil and avocados for healthy fats
Answer: Comprehensive overview of foods with mitochondrial repair benefits
The most effective foods to repair and activate mitochondria include wild salmon, spinach, broccoli, blueberries, nuts, and olive oil. These deliver antioxidants that combat oxidative stress and support the electron transport chain. Ditching processed ingredients and embracing whole, colorful food sources provides the variety of nutrients required for mitochondrial biogenesis and optimal enzyme function.
People Also Ask: How to reverse mitochondrial dysfunction?
Key approaches to support and rejuvenate mitochondria
Make dietary changes—eliminate processed foods, increase phytonutrient intake
Use targeted supplementation after consulting a healthcare provider (CoQ10, PQQ, omega-3s)
Reduce stress and practice restorative activities like mindful breathing and regular sleep routines
Answer: Step-by-step guide to reversing mitochondrial dysfunction
Reversing mitochondrial dysfunction starts with adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, exercising regularly, and restoring circadian balance through sleep hygiene. For persistent symptoms, supplementation and professional guidance may be necessary. Over time, these habits can help rebuild damaged electron transport chains and restore healthy cellular energy production.
People Also Ask: What are the symptoms of low mitochondria?
Recognizing early warning signs of mitochondrial issues
Frequent fatigue, muscle pain, and poor exercise recovery
Cognitive difficulties, mood swings, and mental fog
Rapid signs of aging such as hair loss, wrinkles, and decreased immunity
Answer: Explanation of common symptoms linked to poor mitochondrial function
Low mitochondrial output manifests as constant tiredness, weakness in skeletal muscle, compromised mental clarity, and slower healing from illness or injury. Persistent low energy or inability to recover from normal daily stress may signal the need for focused mitochondrial support and lifestyle adjustments.
Frequently Asked Questions About How to Activate Mitochondria
How long does it take to activate mitochondria?
With consistent changes in diet, exercise, and sleep, many people report improved energy levels in as little as 2 to 4 weeks, though full cellular adaptation can take a few months.Are supplements safe for everyone?
Most mitochondrial-supportive supplements are safe for healthy adults, but individuals with medical conditions or those on medication should always consult a medical professional first.Can children benefit from supporting their mitochondria?
Yes! A healthy lifestyle rich in nutrients and movement helps children with energy, focus, and development, though supplement protocols should be age-appropriate and doctor-approved.Is mitochondrial dysfunction reversible?
While severe, inherited mitochondrial disorders may not be curable, most cases of dysfunction resulting from lifestyle and environment can be reversed with sustained changes in nutrition, movement, and stress management.
Key Takeaways: How to Activate Mitochondria for Optimal Health
Invest in nutrient-rich whole foods and regular physical activity
Reduce toxin exposure and chronic stress for cellular defense
Explore supplements and cutting-edge therapies for advanced support
Start with one new healthy habit today—and build your vitality from the inside out
Ready to Activate Your Mitochondria? Start Small—Choose One Strategy Today
The science is clear: when you make your mitochondria stronger, your energy and longevity soar. Pick one actionable step from this guide and start building lasting health—your future self will thank you.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment