In recent years, the beauty industry has witnessed a jaw-dropping transformation: global sales of anti-aging collagen supplements have tripled in just five years, outpacing countless other skincare trends. This isn’t just hype—there’s an explosive surge of consumer trust behind these products, with millions seeking fresher, more youthful skin. But does anti-aging collagen really deliver on its promises, or is it another fleeting beauty fad? This deep dive unpacks the science, opinions, and real-life results—giving you the facts before you invest in your next bottle.

A Surprising Statistic: Anti-Aging Collagen’s Growing Popularity
The numbers don’t lie. Anti-aging collagen has rapidly moved from niche wellness forums into the mainstream, becoming a staple in beauty routines across the globe. From medical spas to supermarket shelves, collagen supplements and associated products have gained widespread attention for their potential to improve skin hydration, combat fine lines, and boost overall skin elasticity.
The shift is not just anecdotal. According to recent market data, the collagen supplement industry has seen exponential growth, especially as controlled trials and human studies begin to support some of its key claims. This sharp rise signals a collective hope: can supplementing with collagen peptides and hyaluronic acid help us to maintain healthy, youthful skin and perhaps intervene in the visible processes of aging?
Unpacking the Surge: Why Anti-Aging Collagen Is Everywhere
Fueling this global interest is the frequent buzz on social media, endorsements from influencers, and a steady drumbeat of emerging research—making anti-aging collagen products must-have essentials for many. As more evidence surfaces about the effects of collagen and the importance of amino acids for skin health, consumer confidence only grows. Companies tout their products as solutions not only for fine lines and wrinkles but for overall improvements in skin smoothness and radiance.
"Recent industry reports show global sales of collagen supplements have tripled in the last five years—demonstrating a dramatic surge of trust in anti-aging collagen products."
What You’ll Learn from This Deep Dive into Anti-Aging Collagen
Before you choose the next collagen product for your shelf, it’s essential to understand what these supplements can realistically achieve—and where their limitations lie. This article will equip you with unbiased insights and evidence-based answers to your most pressing questions about anti-aging collagen.
The scientific rationale behind anti-aging collagen claims
How different types of collagen supplements compare
Potential benefits and realistic expectations
Expert opinions and research-backed facts
Considerations on side effects and safety of anti-aging collagen
Understanding Anti-Aging Collagen: A Comprehensive Guide

What is Anti-Aging Collagen?
To start, collagen is the most abundant protein in our bodies—accounting for nearly 30% of total protein content. It acts as the building block for skin, hair, nails, tendons, and even bones. As we age, our natural collagen production slows dramatically, manifesting as fine lines, wrinkles, and reduced skin elasticity. Anti-aging collagen products are designed to replenish these dwindling reserves, providing the raw materials (amino acids) necessary to help repair and maintain skin structure. These supplements typically come in powder, capsule, or beverage form, making them accessible in modern routines focused on skin health and vibrancy.
While not all collagen is created equal, most supplements use hydrolyzed collagen peptides—meaning the protein is broken down into smaller, more easily absorbed fragments. This process, called hydrolysis, makes it possible for the body to use the collagen more efficiently. Whether taken as a powder stirred into your smoothie or in capsule form, these products promise to improve skin smoothness and reduce visible aging when combined with a balanced diet and consistent skincare rituals.
Collagen Supplement vs. Collagen Supplements: Clarifying the Basics
The terms collagen supplement and collagen supplements can be confusing, but both refer to orally consumed products containing various types of collagen—Type I and Type III are most common for skin, while Type II is often aimed at joint support. Most products combine these with supporting ingredients such as hyaluronic acid or vitamin C to boost absorption and effectiveness. Users should review product labels for hydrolyzed forms, which are generally linked to better results in human studies. Ultimately, understanding these distinctions helps consumers pick supplements that best fit their needs—whether targeting skin, hair, nails, or even joint health.
How Does Anti-Aging Collagen Work Inside Your Body?
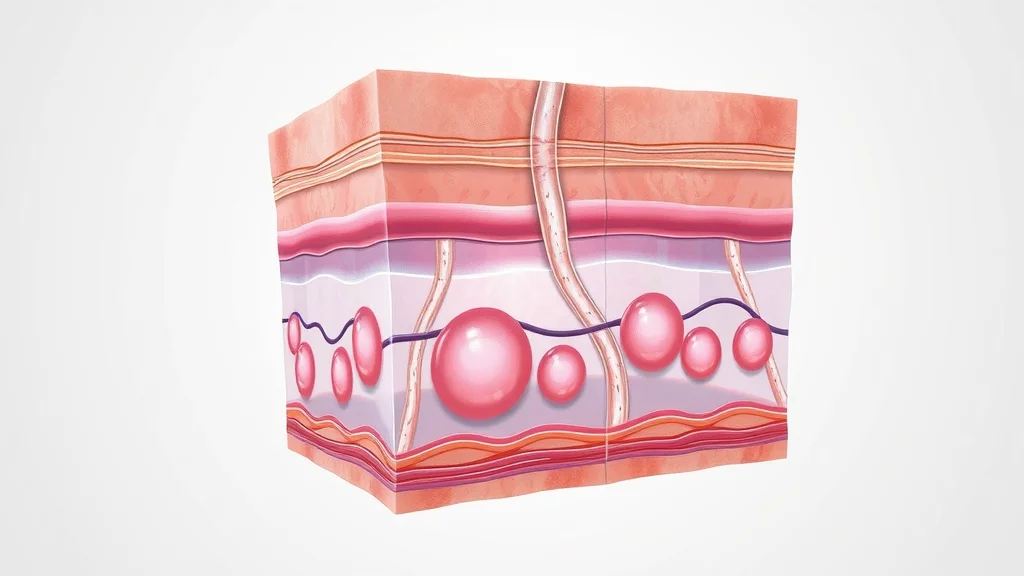
Collagen Peptide and the Science of Skin Elasticity
When you ingest collagen peptides, your digestive system breaks them down into amino acids, which are then absorbed and distributed throughout the body. Theoretically, these amino acids serve as vital building blocks—helping your skin synthesize new collagen and replace what’s naturally lost with age. Studies show that consistent supplementation can lead to visible improvements in skin hydration and elasticity, reducing the appearance of fine lines. The science lies in triggering your body’s fibroblasts to ramp up collagen generation, which supports a plumper, more youthful complexion.
What makes hydrolyzed collagen particularly promising is its proven bioavailability. This means your body can actually use it—unlike some larger protein molecules that are simply broken down and excreted. Supplementing with a peptide complex has, in some studies, helped to maintain skin smoothness and restore bounce, indicating that the effects of collagen stretch beyond mere hype and into the realm of measurable, visible benefits.
Human Studies on Collagen Products and Skin Hydration
Controlled trials have provided promising data on the skin hydration benefits of oral collagen supplements. Participants who consumed hydrolyzed collagen or collagen hydrolysate daily over eight to twelve weeks reported not only better moisture retention but also improved softness and reduced fine lines compared to a control group. These human studies consistently highlight the synergy between collagen supplementation and supportive ingredients like hyaluronic acid.
However, not every study agrees on the magnitude of results or the best type of collagen for anti-aging. Some evidence is stronger for Type I and Type III for skin, while Type II is more closely linked to joint health. Variables like age, baseline skin condition, and the specific formulation can all influence outcomes. So while early clinical evidence points to a real impact—particularly for hydration and elasticity—individual responses do vary.
Comparison Table: Collagen Types and Their Claimed Benefits | |||
Type of Collagen |
Common Source |
Main Claimed Benefits |
Found In |
|---|---|---|---|
Type I |
Bovine, Marine |
Skin elasticity, reduced fine lines, healthy hair & nails |
Most skin-targeted supplements |
Type II |
Chicken |
Joint health, cartilage support |
Joint-specific supplements |
Type III |
Bovine |
Skin firmness, vascular health |
Often paired with Type I in skin formulas |
Key Ingredients: Hyaluronic Acid, Collagen Peptide, and Beyond

The Role of Hyaluronic Acid in Skin Hydration and Youthfulness
While collagen peptides are central to most anti-aging formulas, hyaluronic acid is a critical co-star. Known for its incredible ability to attract and retain moisture, hyaluronic acid helps your skin stay supple and plump. It complements collagen’s supportive functions by boosting skin hydration and mitigating the loss of bounce and elasticity that come with aging. When these ingredients are combined in a single collagen supplement, the synergistic effects can produce more noticeable improvements in both texture and radiance.
Many high-quality products pair hydrolyzed collagen with additional active components such as vitamin C, which plays a vital role in collagen synthesis. Others include peptide complex blends or antioxidants to further protect skin from damage. Choosing a supplement that unites these scientifically-backed ingredients may help you maximize the visible effects of collagen supplementation.
Are Collagen Peptides Superior for Anti-Aging?
Not all sources or forms of collagen are created equal—but most studies focus on collagen peptides (hydrolyzed collagen) due to their high absorption and bioavailability. Considered superior to other forms, peptides are rapidly taken up by the body and can directly support the skin’s underlying structure.
The emerging consensus? If you’re looking for targeted anti-aging effects, prioritize supplements listing “hydrolyzed collagen” or “collagen peptides” high on the ingredient list—especially when combined with hyaluronic acid or vitamin C. Clinical data suggests these combinations outperform standalone products for skin hydration, firmness, and minimizing lines and wrinkles.
Oral Collagen vs. Topical Collagen: Which Delivers Better Results?

Oral Collagen Supplement: What the Science Says
Oral collagen supplements—ingested as powders, capsules, or beverages—are at the forefront of most controlled trials on anti-aging. Studies demonstrate that after ingestion, collagen peptides are absorbed into the bloodstream, where they can prompt new collagen generation in the skin’s dermal layer. This mechanism directly supports skin hydration and skin elasticity, with users in clinical studies often noticing reductions in fine lines and visible dryness.
The distinction between oral and topical forms is significant. Oral collagen is believed to have systemic benefits, meaning it can target not only your face but also joints and connective tissue. However, real-world results depend on the type of collagen, whether hydrolyzed, the presence of supporting substances like hyaluronic acid, and an individual’s baseline collagen levels. For best results, users are advised to combine a consistent oral collagen supplement routine with a nutrient-rich diet and healthy lifestyle.
Topical Collagen: Myths vs. Facts
While topical creams and serums with collagen are widely marketed for their moisturizing effects, the scientific evidence supporting their ability to actually integrate with the skin’s deeper structure is far weaker than with oral options. Collagen molecules are typically too large to penetrate the outermost layer of the skin (epidermis), limiting their anti-aging impact to surface-level hydration rather than supporting long-term elasticity or wrinkle reduction.
This isn’t to say topical products aren’t beneficial—they can temporarily improve skin hydration and confer a smoother look when combined with other ingredients. But when it comes to robust, measurable improvements in elasticity, the current clinical consensus points to oral supplementation as the more effective route.
"While topical products may improve temporary skin hydration, controlled trial evidence leans toward oral collagen for measurable shifts in elasticity."
Exploring the Benefits of Anti-Aging Collagen
Skin Hydration, Skin Elasticity, and More: Effects of Collagen
Arguably, the most celebrated benefits of collagen include improvements in skin hydration and elasticity. Regular supplementation—especially with the addition of hyaluronic acid—has been shown to increase water retention in the skin, making it look plumper and smoother. Controlled trials highlight noticeable reductions in fine lines and wrinkles after 2–3 months of consistent use, especially among individuals whose baseline collagen levels have declined with age.
Collagen supplementation may also contribute to stronger nails, shinier hair, and more resilient joints by delivering amino acids that play a critical role in these connective tissues. Users often report a cascading array of benefits: enhanced skin smoothness, fewer brittle nails, and even more flexible joints. While no supplement can halt aging, the effects of collagen are supported by a growing body of research and real-world testimonials.

Are All Collagen Supplements Created Equal?
Not every collagen supplement on the market is of equal quality. The best results are associated with hydrolyzed collagen peptides, third-party testing for purity, and combinations that include not just collagen but also nutrients such as hyaluronic acid and vitamin C. Careful label reading is essential, as some products use unproven forms or filler ingredients. Look for clinical data, controlled trial backing, and endorsements from health professionals.
It’s also important to set realistic expectations. Genetics, lifestyle, and your baseline diet all affect how much benefit you’ll gain, even when taking a high-quality collagen supplement. Consistency is key—improvements in skin hydration and elasticity build over weeks and months, not overnight.
Collagen Products for Joint, Nail, and Hair Health
While the primary focus of most anti-aging collagen formulas is skin, many consumers notice collateral benefits such as less brittle nails and shinier, more robust hair. Type II collagen, often sourced from chicken, is especially popular for joint support. Combined peptide complexes may serve multiple functions, helping not only to improve skin smoothness but also to support healthy cartilage and connective tissue throughout the body. This versatility helps cement collagen’s role as a staple for those seeking total-body wellness beyond the surface.
When choosing a collagen supplement for these additional benefits, be sure it features the specific types of collagen associated with your health priority—Type I/III for skin and nails, and Type II for joint support. As always, consulting with a healthcare provider ensures you select a product that aligns with your body’s specific needs and any existing conditions.
Potential Drawbacks and Side Effects of Anti-Aging Collagen

Reported Side Effects: What You Should Know
As with any supplement, collagen is not entirely without risk. While most users tolerate oral collagen supplements well, some individuals report mild side effects such as digestive upset, a lingering aftertaste, or fullness. It’s important to follow dosing instructions and start with a lower dose if you’re new to collagen products. Clinical trials suggest that adverse effects are rare, but not impossible—especially in those with allergies or sensitivities to protein-rich foods like beef, chicken, or fish from which collagen is derived.
Commonly reported side effects, though infrequent, include bloating, a feeling of heaviness, or mild gastrointestinal changes. These are typically short-lived and resolve with reduced dosage or product switching. Still, it’s always prudent to keep a close eye on your body’s reactions.
Safety and Allergic Reactions to Collagen Supplements
The biggest safety concern for collagen supplements is potential allergic reactions—especially for those sensitive to specific animal proteins. Since most products are derived from bovine, marine, or chicken sources, reviewing ingredient lists is crucial if you have any known allergies.
Additional concerns can arise from contamination or low-quality manufacturing processes, making third-party lab tested supplements a safer bet. Pregnant, breastfeeding, or chronically ill individuals should consult a healthcare provider before starting collagen supplements. Vigilance is especially critical if you notice any signs of adverse effects or allergic response.
Expert Opinions: Do Collagen Supplements Live Up to The Hype?
Dermatologists and nutritionists generally agree that anti-aging collagen can support better skin hydration and elasticity, with clinical data to support modest benefits when formulas are high quality. However, experts caution that not all products are equal—highlighting the need for more large-scale human studies and standardized research. As the field evolves, smart consumer choices and realistic expectations are essential.
"Evidence from recent controlled trials is promising—but not all anti-aging collagen products are created equal, and more human studies are needed for robust claims."
The takeaway? Select supplements, prioritize those that are hydrolyzed and third-party tested, and watch this space for even more data as science continues to unfold.
People Also Ask About Anti-Aging Collagen
Which collagen is best for skin anti-aging?
The best collagen for skin anti-aging is typically Type I and Type III collagen, ideally in hydrolyzed or peptide form for better absorption. Marine-sourced collagen is often especially prized for its high bioavailability and proven effects in clinical research on skin hydration and elasticity. Look for supplements with added hyaluronic acid and vitamin C for optimal results.
Does collagen really help with anti-aging?
While no supplement can completely halt aging, consistent use of high-quality collagen supplements has been shown in controlled trials to improve skin hydration, elasticity, and reduce the appearance of fine lines. Scientific evidence, though still evolving, generally supports modest visible improvements when included as part of a holistic skincare and nutrition approach.
Will I look younger if I take collagen?
Many users report a fresher appearance and plumper skin after regular collagen supplementation, thanks to better hydration and elasticity. However, individual results vary based on age, skin condition, and lifestyle. Collagen is best viewed as a tool for supporting youthful skin—results are subtle, cumulative, and most significant with consistent use over weeks or months.
At what age should you take collagen?
Collagen production begins to decline in our mid-to-late twenties, so starting supplementation in your late twenties or thirties can be beneficial for prevention and maintenance. However, people of any age may see improvements in skin hydration, elasticity, and hair or nail health by introducing a collagen supplement into their routine.
Essential Tips for Choosing an Effective Anti-Aging Collagen Supplement

Prioritize products with hydrolyzed collagen peptides
Look for third-party testing for purity and safety
Choose supplements that also feature hyaluronic acid
Review controlled trial-backed claims, not marketing hype
Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice
FAQs: Anti-Aging Collagen Supplements
How long before I see results with anti-aging collagen?
Most users start noticing improved skin hydration and elasticity within 8 to 12 weeks, though some may see subtle changes sooner.Are there vegan alternatives to collagen supplements?
While vegan collagen is not identical to animal-derived collagen, certain plant-based peptides and amino acid blends aim to support natural collagen production.Can I combine collagen with other skincare ingredients?
Yes, combining collagen with ingredients like hyaluronic acid or vitamin C is often recommended for synergistic effects.Should I take collagen with or without food?
Collagen supplements are usually safe to take with or without food, but always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines or your healthcare provider’s advice.
Key Takeaways: Is Anti-Aging Collagen Worth Considering?
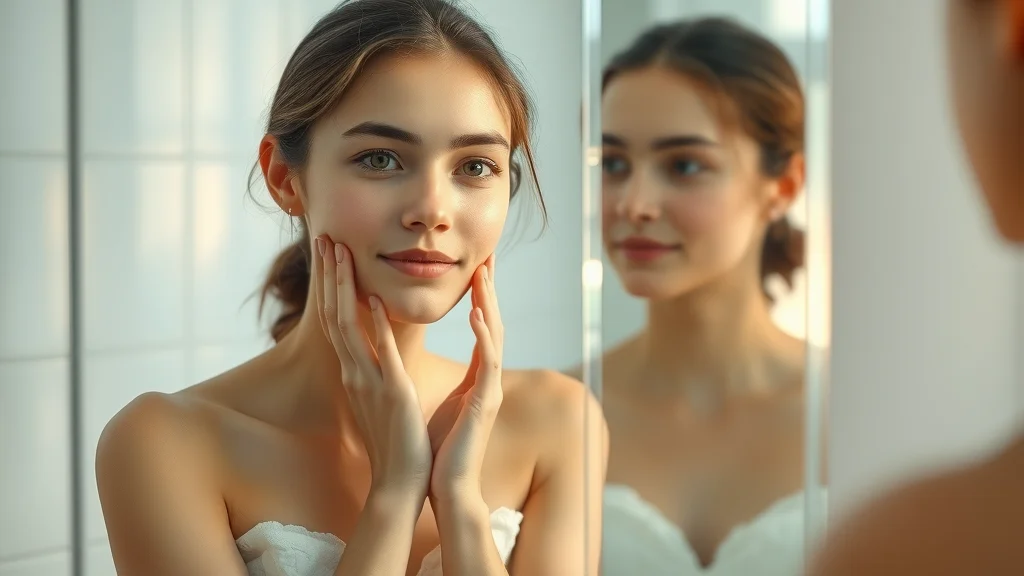

Anti-aging collagen, especially hydrolyzed forms, shows promise
Skin hydration and elasticity improvements are supported by evidence
Results depend on quality, formulation, and individual factors
Expert consensus highlights the need for more large-scale human studies
Ready to Experience the Potential of Anti-Aging Collagen?
Interested in experiencing the benefits of anti-aging collagen firsthand? Start by choosing a quality supplement and consulting your healthcare professional for tailored advice. There’s never been a better time to make informed decisions for your skin’s future.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment